One of the most common pathologies of the musculoskeletal system is the arthrosis of the knee joint (otherwise gonar rose) a chronic disease accompanied by dystrophy and the destruction of the joint structures of the knee.
The result of destructive processes is a sharp restriction or a complete loss of common mobility and consequently - a decrease in performance, disability.
It is possible to prevent adverse consequences if they are diagnosed early and are therapy in good time.
Reasons
According to origin, the knee arthrosis is primary and secondary.Primarily develops as an independent disease, is more often diagnosed in older people and in this case is due to age -related changes that occur in the tissues.Secondary gonarthrosis becomes the result of other diseases and disorders in the body.
The development of gonarthrosis carries:
- Injuries (transfers, fractures, meniscus damage);
- Diseases of the musculoskeletal system (congenital deformation of the legs, kniedysplasia, chondrocalcinosis, arthritis, osteoporosis);
- Constant high loads of the joint due to professional activities, professional sport;
- Obesity, obesity;
- Endocrine diseases, including diabetes, hypothyroidism, acromigaly;
- Metabolic disorders;
- Genetic predisposition.
Symptoms
Inflammation with osteoarthritis of the knee joint is accompanied by two main clinical manifestations - pain and edema.The intensity and frequency of the analysis of pain depends on the damage to the joint structures.In the early stages, only pain with a load can be felt and quickly passed in peace.With advanced gonarthrosis, painful pain is constantly present during the movements with a change in the weather.
Other signs of osteoarthritis of the knee joint:
- Crunch when moving;
- Stiffness in the joint, violation of the motor function;
- The deformation of the knee (with neglected gonarthrosis).
Gonarthrosis can be accompanied by synovitis (accumulation of liquid in the joint cavity) and the subsequent formation of a bakery cyst (elastic education on the back of the knee).
Degree of arthrosis
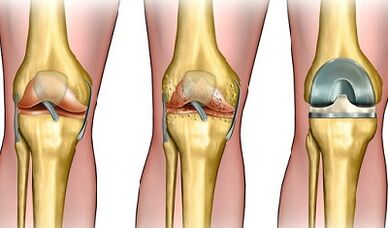
The symptoms of arthrosis of the knee joint differ depending on the damage to the structures of the knee, and therefore the 3 stages of pathology are differentiated.
- Arthrosis of the knee joint 1 degreeIt manifests itself through weak pain at loads (in peace at the same time) with a slight rigidity after sleep.In the radiological image, an insignificant narrowing of the common gap (less than a third) is narrowed, the presence of individual osteophytes (bone growth).
- Arthrosis of the knee joint 2 degreesIt is accompanied by pain and characteristic crunch during the movements.The pain remains alone for some time.Morning stiffness, restriction of the amplitude of the movements has been determined.Diagnostic procedures show a pronounced narrowing of the common gap (more than half) and several osteophytes.
- Arthrosis of the knee 3 degreesIt is accompanied by constant painful pain that intensify during the movements and at night.The morning stiffness remains for more than an hour with an tightening of the inflammation and at least half an hour - during the remission times.The mobility of the joint is very limited or completely lost.Several large osteophytes, cysts are visible in the radiological picture.The joint column is constricted by more than two Thöke from the standard.
Depending on the degree of arthrosis of the knee joint, conservative or surgical treatment is prescribed to the patient.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of the arthrosis of the knee joint includes visual examination, analysis of the patient's symptoms, laboratory test (urine analysis, general and biochemical blood tests) and instrumental examination methods.
With the following diagnostic methods you can confirm or refute the diagnosis:
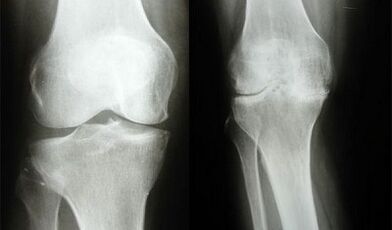
- Radiography;
- Ultrasound (ultrasound);
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging);
- CT (computer tomography);
- Arthroscopy and scintigraphy (with suspicion of a tumor).
With these methods, it is possible to recognize the narrowing of the joint column, thinning and deformation of the cartilage, the presence of liquid in the joint cavity, structural changes in the synovial membrane, the growth of osteofitis and the ossification of the cartilage, the growth of osteofitis and cartilage.
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment methods can reduce pain and inflammation, improve the blood circulation and nutrition of peristified tissue and strengthen muscle apparatus.
For this purpose you will be recorded:
- Medicine therapy;
- Blockade;
- Physiotherapy and manual therapy;
- Medical physical education.
An important part of the treatment of osteoarthritis is compliance with a therapeutic diet.
The conservative treatment of the arthrosis of the knee joint will be effective in the early stages of the disease if slight dystrophic cartridges of cartilage, inflammation and impaired functions of the synovial bowl are found.
Drugs
The drug treatment includes the appointment:
- Non -steroidal anti -inflammatory medication (NSAIDS);
- Chondroprotectors;
- Hyaluronic acid.
NSAID
Non -steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs relieve inflammation, reduce their main symptoms and pain.
Preparations are prescribed in the form of solutions (for intramuscular administration) or tablets, capsules (for oral administration).Capsules and tablets from the osteoarthritis of the knee joint of the NSAID group are carried out in short courses, since the medication have a strong irritating effect on the stomach mucosa and can provoke the development of peptic ulcers, have many other side effects.
Additionally prescribed external medicines (ointments, gels, creams) based on non -steroidal inflammatory components.Local therapy may be carried out longer.
NSAIDs have a pronounced anti -inflammatory effect, but with longer use contributes to the further destruction of cartilage.
NSAIDS are symptomatic therapy.However, they contribute to eliminating unpleasant symptoms of the disease, but do not influence the condition of the cartilage.In contrast to these products, chondroprotectors and hyaluronic acid accelerate the processes of regeneration of cartilage tissue and slow down the destruction.
Chondroprotectors
The medication of the chondroprotectors group contains chondroitine and glucosamine (structural cartilage elements) and help to restore the knee with osteoarthritis of the knee joint.They are available in the form of tablets, powder for oral administration, an injection solution.
The minimum taking tablets and powder is 3 months.After a break, the course is repeated 2-3 times.The course of treatment with a solution comprises 12-15 injections and repeated 2-3 times a year.
The first positive results of treatment with chondroprotectors can be felt just a few months after the therapy begins.
Hyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid is inserted into the affected connection.The healing of the arthrosis of the knee joint plays the role of lubrication - envelops the articular surfaces and thus reduces the friction between them.
Therapy with hyaluronic acid helps to increase the elasticity of cartilage tissue and prevents the further destruction of the joint structures that improve the mobility of the joint and the symptoms of inflammation are reduced.Medicines are well tolerated, do not cause side effects.The only disadvantage is the high costs.
The course of treatment with hyaluronic acid usually includes 3-4 injections that are carried out with breaks of 10 to 14 days.
blockade
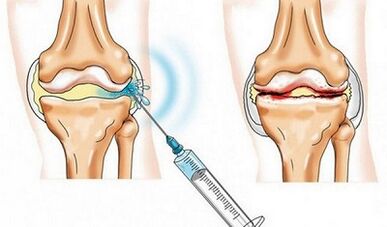
If it is not possible with non -steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs to relieve knee pain with osteoarthritis, a blockade is carried out -a treatment method in which the medication is injected directly into the affected tissue in order to relieve pain and inflammation.In the therapy of osteoarthritis, joint (injections in the joint cavity) and periary blockade (in the periartic cavity) are used.
The main advantage of the method is an immediate targeted effect, since with such an introduction, the maximum concentration of the active substance is generated exactly in the inflammatory zone.In addition, medication does not fall into the systemic blood circulation, which significantly reduces the risk of side effects.
In the later stages of gonar rose, the joint column narrows, osteophytes grow, common surfaces are deformed, so only a periricular blockage is permitted.
The blockage of the knee joint for osteoarthritis can be carried out using anesthetics and corticosteroids.
The anesthetics are usually introduced in combination with steroid hormones to reduce the pain of the procedure.
Hyaluronic acid and chondroprotectors can also be inserted directly into the joint.In this case, however, we do not talk about blockade, but about the intra -karticular injection, since these drugs do not block pain pulse, but trigger the processes of regeneration of cartilage tissue.
Physiotherapy and manual therapy
The main methods for physiotherapy effects used in the treatment of osteoarthritis are:
- Laser treatment;
- Ultrasonic therapy;
- Cryotherapy;
- Therapy with paraffin and ozokerite;
- Dirt.
The main task of all physiotherapeutic methods is to stimulate the blood circulation in nearby tissues and to improve the nutrition of the cartilage.
Training therapy
Pain syndrome forces a patient with gonar rose to limit motor activity, with the nearby ligaments and muscle atrophy.This condition has a negative effect on the articular fabric, since the nutrients penetrate the cartilage from the synovial fluid during movement.When the joint is constantly in peace, dystrophic processes are tightened.

For this reason, physiotherapy exercises are an integral part of conservative therapy.With moderate physical activity you can strengthen the muscle device, improve the power of joint structures, eliminate stiffness and improve the motor function of the knee.
The exercises of the therapeutic exercises are developed individually by the doctor for each patient, whereby the depth of the lesion and the functional condition of the joint structures are taken into account.
General recommendations for carrying out training therapy for the arthrosis of the knee joint:
- Start the lessons only after signs of acute inflammation have been stopped.
- Perform all exercises smoothly, without sudden movements;
- The load is gradually increased;
- Eliminate high loads of the connection (improved flexion/expansion of the knee);
- If pain or symptoms occur, they stop training.
diet
With gonarthrosis, products that:
- Amino acids (dairy products, low -fat meat varieties);
- Collagen (dishes with gelatin);
- Irreplaceable fatty acids (vegetable oils, fish);
- Sulfur and selenium (legumes, grain, cabbage and apples, beef, chicken, eggs).
It is also important:
- Eliminate the use of smoked meat, cucumbers, marinades;
- Limit salt consumption;
- hold a 5-fold diet;
- Watch drinking mode.
Excess body weight is one of the main factors that cause the development of osteoarthritis of the knee joint.Therefore, the task of patients with excess weight is a decrease in body weight.In this case, you can only achieve the result with the help of a diet, since intensive sports for the inflamed joint are harmful.
In order to reduce body weight, it is recommended to rule out the menu:
- Fats of meat and fish;
- Cream, homemade sour cream and other dairy products with a high proportion of fat content;
- Margarine, mayonnaise, different sauces;
- Confectionery;
- Fast food;
- Sweet drinks.
Surgical treatment

The osteoarthritis of the knee joint of the 3rd degree is not accessible to conservative therapy, so surgery is the only way out for the patient.
There are two options for surgical intervention:
- Correction osteotomy- is carried out in the early stages of the development of the 3rd stage of gonarthrosis.If the cartilage is partially destroyed, it is possible to remove osteophytes.
- Endoprosthetics- The replacement of the joint or the destroyed parts is carried out with the complete destruction of the cartilage.
forecast
Pathological changes in common structures are progressive, irreversible.With the early diagnosis and proper treatment, however, you can completely stop the inflammation and dystrophic changes in the cartilage tissue - osteoarthritis of the knee joint of the 1st degree, well for conservative therapy.
With the osteoarthritis of the 2nd degree, which is accompanied by the destruction of the cartilage and the formation of osteophytes, conservative methods enable you to slow down or suspend cartilage, to stop inflammation and to improve motor activity.However, doctors are often forced to use blockade and arthroscopy.
It is impossible to heal the osteoarthritis of the knee joint of 3 degrees in a conservative way.The only way to restore the mobility of the knee is surgical intervention.